
SCARS Institute’s Encyclopedia of Scams™ Published Continuously for 25 Years

SCARS™ Guide: The Difference Between Spam Emails And Phishing Emails
In The World Of Scams, Terms Are Often Confused And Then Shared Incorrectly
This creates confusion over what we mean when we talk about specific scams, such as spam emails and the various types of phishing emails.
First – We Hate Them Both
Although both spam emails and phishing emails are unwanted incoming communications, they are completely different.
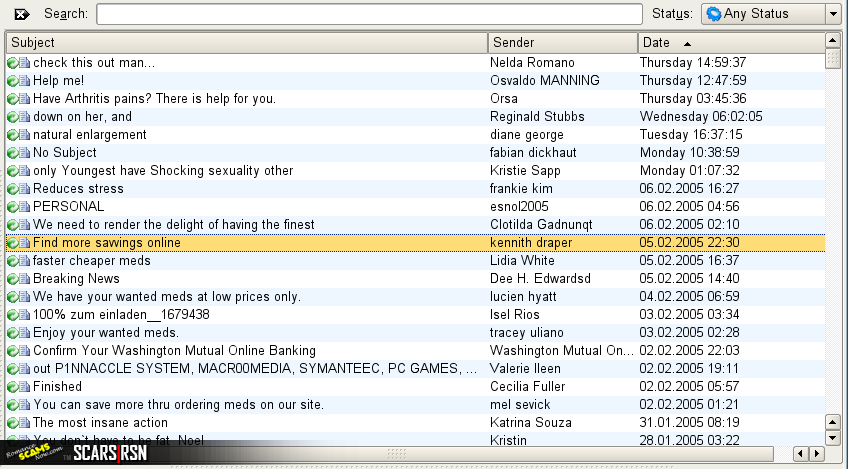
SPAM EMAILS
Email spam, also known as junk email, is unsolicited messages sent in bulk by email (spamming).
Spam email is unauthorized marketing or advertising communication sent to your inbox. Most spam is honest – providing an offer or advantage for legitimate product or service. However, not all spam is honest. A significant percentage of spam are scams! Scams as in the garden variety of fraud – misrepresentations or outright cons.
The name comes from Spam luncheon meat by way of a Monty Python sketch in which Spam is ubiquitous, unavoidable and repetitive. Yes, Monty Python names spam!
Email spam has steadily grown since the early 1990s, and by 2014 was estimated that it made up around 90% of email messages sent. Since the expense of the spam is borne mostly by the recipient (in the form of time spent screening, sorting, and disposing of), it is effectively postage due advertising. This makes it an excellent example of a negative externality.
The legal definition and status of spam vary from one jurisdiction to another, but laws and lawsuits have nowhere been particularly successful in stemming spam. Though the SCARS Proposal for Changes to the U.S. CDA Law » may positively impact it.
Most email spam messages are commercial in nature. Whether commercial or not, many are not only annoying but also dangerous because they may contain links that lead to phishing web sites or sites that are hosting malware – or include malware as file attachments. [see below]
Spammers collect email addresses from chat rooms, websites, customer lists, newsgroups, and viruses that harvest users’ address books. These collected email addresses are sometimes also sold to other spammers.
Spam filters were built to capture these emails. Think of what is currently in your Spam filter. You have people selling you things that you didn’t ask for, or emails that make zero sense. Recipients of spam most likely had their email addresses obtained by spambots. These are automated programs that crawl the internet looking for email addresses. From there, spammers create email distribution lists and send emails to millions of addresses. Some examples of spam emails are weight loss programs, discounted pharmaceuticals, or job opportunities.
419 SCAM EMAIL
You are all familiar with the Nigerian Prince style emails. Offering millions in exchange for a small Advance Fee. Of course, these are scams and easy to recognize. Much harder are some of the more subtle forms of these.
An advance-fee scam is a form of fraud and one of the most common types of confidence tricks usually sent via email. The scam typically involves promising the victim a significant share of a large sum of money, in return for a small up-front payment, which the fraudster requires in order to obtain the large sum. If a victim makes the payment, the fraudster either invents a series of further fees for the victim or simply disappears. According to the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI), “An advance fee scheme occurs when the victim pays money to someone in anticipation of receiving something of greater value—such as a loan, contract, investment, or gift—and then receives little or nothing in return.”
There are many variations of this type of scam, including the 419 scam (also known as the Nigerian Prince scam), the Spanish Prisoner scam, the black money scam, Fifo’s Fraud, and the Detroit-Buffalo scam. The scam has been used with fax and traditional mail and is now prevalent in online communications like emails.
While Nigeria is most often the nation referred to in these scams, they originate in other nations as well. Other nations known to have a high incidence of advance-fee fraud include: Ivory Coast, Togo, South Africa, the Netherlands, and Spain. The number “419” refers to the section of the Nigerian Criminal Code dealing with fraud, the charges, and penalties for offenders.
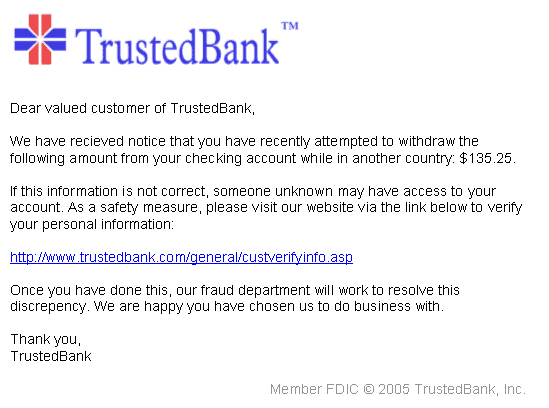
PHISHING EMAILS
Phishing is the fraudulent attempt to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by disguising as a trustworthy entity in electronic communications – usually email. Typically carried out by email spoofing or instant messaging, it often directs users to enter personal information at a fake website, the look and feel of which are identical to the legitimate site.
Phishing is an example of social engineering techniques being used to deceive users. Users are often lured by communications purporting to be from trusted parties such as social websites, auction sites, banks, online payment processors or IT administrators, etc.
The word itself is based on the metaphor fishing, due to the similarity of using bait in an attempt to catch a victim.
Phishing emails are emails with malicious intent sent from scammers posing as a legitimate source. These emails demand action from the end user. Scammers mimic the emails, forms, and websites of legitimate people or companies in an effort to lure people into providing their private, personal information. For example, credit card numbers, social security information, account logins, and personal identifiers or pins. The victim usually doesn’t realize they’ve been compromised until long after the event. Oftentimes the victim does not realize they have fallen into a trap until their finances are affected.
The three types of phishing attacks are:
- Spear Phishing – Spear phishing is a targeted phishing attack directed at a specific individual.
- Clone Phishing – Clone phishing is where a legitimate, and previously delivered, an email containing an attachment or link has had its content and recipient address(es) taken and used to create an almost identical or cloned email.
- Whaling – Whaling is an attack targeted at a high profile individual.
Not all phishing attacks require an email or a fake website. Messages that claimed to be from a bank told users to dial a phone number regarding problems with their bank accounts. Once the phone number (owned by the phisher, and provided by a voice over IP service) was dialed, prompts told users to enter their account numbers and PIN. Vishing (voice phishing) sometimes uses fake caller-ID data to give the appearance that calls come from a trusted organization.
Other Techniques
Another attack used successfully is to forward the client to a bank’s legitimate website, then to place a popup window requesting credentials on top of the page in a way that makes many users think the bank is requesting this sensitive information.
Tabnabbing takes advantage of tabbed browsing, with multiple open tabs. This method silently redirects the user to the affected site. This technique operates in reverse to most phishing techniques in that it does not directly take the user to the fraudulent site, but instead loads the fake page in one of the browser’s open tabs.
ENFORCEMENT & CONTROL
Attempts to deal with phishing incidents include legislation, user training, public awareness, and technical security measures — because phishing attacks also often exploit weaknesses in current web security.

SCARS™ Team
A SCARS Division
Miami Florida U.S.A.
TAGS: Spam Email, Scam Email, Phishing Email, Tabnabbing, Clone Phishing, Spear Phishing, Whaling, Vishing, Email Scams, Junk Email,
END
– – –
Tell us about your experiences with Romance Scammers in our Scams Discussion Forum on Facebook »
– – –
FAQ: How Do You Properly Report Scammers?
It is essential that law enforcement knows about scams & scammers, even though there is nothing (in most cases) that they can do.
Always report scams involving money lost or where you received money to:
- Local Police – ask them to take an “informational” police report – say you need it for your insurance
- Your National Police or FBI (www.IC3.gov »)
- The SCARS|CDN™ Cybercriminal Data Network – Worldwide Reporting Network HERE » or on www.Anyscam.com »
This helps your government understand the problem, and allows law enforcement to add scammers on watch lists worldwide.
– – –
Visit our NEW Main SCARS Facebook page for much more information about scams and online crime: www.facebook.com/SCARS.News.And.Information »
To learn more about SCARS visit www.AgainstScams.org
Please be sure to report all scammers HERE » or on www.Anyscam.com »
All original content is Copyright © 1991 – 2020 SCARS All Rights Reserved Worldwide & Webwide – SCARS/Romance Scams Now & SCARS/Society of Citizens Against Relationship Scams are all trademarks of Society of Citizens Against Relationship Scams Incorporated (formerly the Society of Citizens Against Romance Scams)
Legal Notices:
All original content is Copyright © 1991 – 2020 SCARS All Rights Reserved Worldwide & Webwide. Third-party copyrights acknowledge.
SCARS, RSN, Romance Scams Now, SCARS|WORLDWIDE, SCARS|GLOBAL, SCARS, Society of Citizens Against Relationship Scams, Society of Citizens Against Romance Scams, SCARS|ANYSCAM, Project Anyscam, Anyscam, SCARS|GOFCH, GOFCH, SCARS|CHINA, SCARS|CDN, SCARS|UK, SCARS Cybercriminal Data Network, Cobalt Alert, Scam Victims Support Group, are all trademarks of Society of Citizens Against Relationship Scams Incorporated.
Contact the law firm for the Society of Citizens Against Relationship Scams Incorporated by email at legal@AgainstScams.org
-/ 30 /-
What do you think about this?
Please share your thoughts in a comment below!
Table of Contents
LEAVE A COMMENT?
Recent Comments
On Other Articles
- velma faile on Finally Tax Relief for American Scam Victims is on the Horizon – 2026: “I just did my taxes for 2025 my tax account said so far for romances scam we cd not take…” Feb 25, 19:50
- on Reporting Scams & Interacting With The Police – A Scam Victim’s Checklist [VIDEO]: “Yes, this is a scam. For your own sanity, just block them completely.” Feb 25, 15:37
- on Danielle Delaunay/Danielle Genevieve – Stolen Identity/Stolen Photos – Impersonation Victim UPDATED 2024: “She goes by the name of Sanrda John now” Feb 25, 10:26
- on Reporting Scams & Interacting With The Police – A Scam Victim’s Checklist [VIDEO]: “So far I have not been scam out of any money because I was aware not to give the money…” Feb 25, 07:46
- on Love Bombing And How Romance Scam Victims Are Forced To Feel: “I was love bombed to the point that I would do just about anything for the scammer(s). I was told…” Feb 11, 14:24
- on Dani Daniels (Kira Lee Orsag): Another Scammer’s Favorite: “You provide a valuable service! I wish more people knew about it!” Feb 10, 15:05
- on Danielle Delaunay/Danielle Genevieve – Stolen Identity/Stolen Photos – Impersonation Victim UPDATED 2024: “We highly recommend that you simply turn away form the scam and scammers, and focus on the development of a…” Feb 4, 19:47
- on The Art Of Deception: The Fundamental Principals Of Successful Deceptions – 2024: “I experienced many of the deceptive tactics that romance scammers use. I was told various stories of hardship and why…” Feb 4, 15:27
- on Danielle Delaunay/Danielle Genevieve – Stolen Identity/Stolen Photos – Impersonation Victim UPDATED 2024: “Yes, I’m in that exact situation also. “Danielle” has seriously scammed me for 3 years now. “She” (he) doesn’t know…” Feb 4, 14:58
- on An Essay on Justice and Money Recovery – 2026: “you are so right I accidentally clicked on online justice I signed an agreement for 12k upfront but cd only…” Feb 3, 08:16
ARTICLE META
Important Information for New Scam Victims
- Please visit www.ScamVictimsSupport.org – a SCARS Website for New Scam Victims & Sextortion Victims
- Enroll in FREE SCARS Scam Survivor’s School now at www.SCARSeducation.org
- Please visit www.ScamPsychology.org – to more fully understand the psychological concepts involved in scams and scam victim recovery
If you are looking for local trauma counselors please visit counseling.AgainstScams.org or join SCARS for our counseling/therapy benefit: membership.AgainstScams.org
If you need to speak with someone now, you can dial 988 or find phone numbers for crisis hotlines all around the world here: www.opencounseling.com/suicide-hotlines
A Note About Labeling!
We often use the term ‘scam victim’ in our articles, but this is a convenience to help those searching for information in search engines like Google. It is just a convenience and has no deeper meaning. If you have come through such an experience, YOU are a Survivor! It was not your fault. You are not alone! Axios!
A Question of Trust
At the SCARS Institute, we invite you to do your own research on the topics we speak about and publish, Our team investigates the subject being discussed, especially when it comes to understanding the scam victims-survivors experience. You can do Google searches but in many cases, you will have to wade through scientific papers and studies. However, remember that biases and perspectives matter and influence the outcome. Regardless, we encourage you to explore these topics as thoroughly as you can for your own awareness.
Statement About Victim Blaming
SCARS Institute articles examine different aspects of the scam victim experience, as well as those who may have been secondary victims. This work focuses on understanding victimization through the science of victimology, including common psychological and behavioral responses. The purpose is to help victims and survivors understand why these crimes occurred, reduce shame and self-blame, strengthen recovery programs and victim opportunities, and lower the risk of future victimization.
At times, these discussions may sound uncomfortable, overwhelming, or may be mistaken for blame. They are not. Scam victims are never blamed. Our goal is to explain the mechanisms of deception and the human responses that scammers exploit, and the processes that occur after the scam ends, so victims can better understand what happened to them and why it felt convincing at the time, and what the path looks like going forward.
Articles that address the psychology, neurology, physiology, and other characteristics of scams and the victim experience recognize that all people share cognitive and emotional traits that can be manipulated under the right conditions. These characteristics are not flaws. They are normal human functions that criminals deliberately exploit. Victims typically have little awareness of these mechanisms while a scam is unfolding and a very limited ability to control them. Awareness often comes only after the harm has occurred.
By explaining these processes, these articles help victims make sense of their experiences, understand common post-scam reactions, and identify ways to protect themselves moving forward. This knowledge supports recovery by replacing confusion and self-blame with clarity, context, and self-compassion.
Additional educational material on these topics is available at ScamPsychology.org – ScamsNOW.com and other SCARS Institute websites.
Psychology Disclaimer:
All articles about psychology and the human brain on this website are for information & education only
The information provided in this article is intended for educational and self-help purposes only and should not be construed as a substitute for professional therapy or counseling.
While any self-help techniques outlined herein may be beneficial for scam victims seeking to recover from their experience and move towards recovery, it is important to consult with a qualified mental health professional before initiating any course of action. Each individual’s experience and needs are unique, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another.
Additionally, any approach may not be appropriate for individuals with certain pre-existing mental health conditions or trauma histories. It is advisable to seek guidance from a licensed therapist or counselor who can provide personalized support, guidance, and treatment tailored to your specific needs.
If you are experiencing significant distress or emotional difficulties related to a scam or other traumatic event, please consult your doctor or mental health provider for appropriate care and support.
Also read our SCARS Institute Statement about Professional Care for Scam Victims – click here to go to our ScamsNOW.com website.



















Thank you for your comment. You may receive an email to follow up. We never share your data with marketers.