
SCARS Institute’s Encyclopedia of Scams™ Published Continuously for 25 Years

Defending Your Organization Against Email Phishing Attacks – 2024
Guarding the Gate: Strategies to Defend Your Organization from Phishing Attacks and Email Scams
How Scams Work – A SCARS Institute Insight
Authors:
• SCARS Institute Encyclopedia of Scams Editorial Team – Society of Citizens Against Relationship Scams Inc.
• Portions courtesy of the UK National Cyber Security Centre
Article Abstract
Phishing attacks, which use deceptive emails and links to steal sensitive data or deploy malware, remain a major threat to organizations. Defending against these requires a multi-layered approach, combining technological measures like anti-spoofing protocols (DMARC, SPF, and DKIM), robust email filtering, and reducing publicly available information attackers can exploit.
User education is essential but should foster a supportive reporting culture rather than relying on punitive phishing simulations that can erode trust. Additional defenses include multi-factor authentication, limiting access privileges, and maintaining updated systems to block threats. Finally, a clear incident response plan ensures swift action to mitigate damage when attacks succeed. By integrating these strategies, organizations can strengthen their resilience against phishing threats.

Guarding the Gate: Strategies to Defend Your Organization from Phishing Attacks and Email Scams
Portions from UK National Cyber Security Centre’s Phishing attacks: defending your organisation 2024
Introduction – What is a Phishing Attack?
A Phishing attack is when attackers send scam emails (or text messages) that contain links to malicious websites, though it can also be an online ad or other means that sends you there. These websites may contain malware (such as ransomware) which can sabotage systems and organizations. Or they might be designed to trick users into revealing sensitive information (such as passwords), or transferring money.
Phishing emails can hit an organization of any size and type. You might get caught up in a mass campaign (where emails are sent indiscriminately to millions of inboxes), or it could be the first step in a targeted attack against your company or a specific employee. In these targeted campaigns, the attacker uses information about your employees or company to make their messages even more persuasive and realistic. This is usually referred to as spear phishing.
The mitigations described in this guidance are mostly focused on preventing the impact of phishing attacks within your organization, but if you implement these measures, you will be helping to protect the whole of the UK. Setting up DMARC, for example, stops phishers from spoofing your domain (that is, making their emails look like they come from your organization).
There are numerous benefits to doing this:
-
- Your own company’s genuine emails are more likely to reach the recipients’ inboxes, rather than getting filtered out as spam.
- From a reputational aspect, no organization wants its name to become synonymous with scams and fraud.
- The more organizations set up DMARC, the harder it is for the phishers to succeed.
Note: Staff within smaller organizations will also find this NCSC guidance useful, but should refer to the NCSC’s Small Business Guide beforehand.
Why You Need a Multi-layered Approach
Phishing mitigations often place too much emphasis on users being able to spot phishing emails. As we explain below, this approach risks wasting both time and money without improving security. Instead, you should widen your defenses to include technical measures, with user education being just one aspect of your approach. A layered approach means you’ll have multiple opportunities to detect a phishing attack, and then stop it before it causes harm. Some phishing attacks will always get through, so you should plan for incidents which means you can minimise the damage they cause.
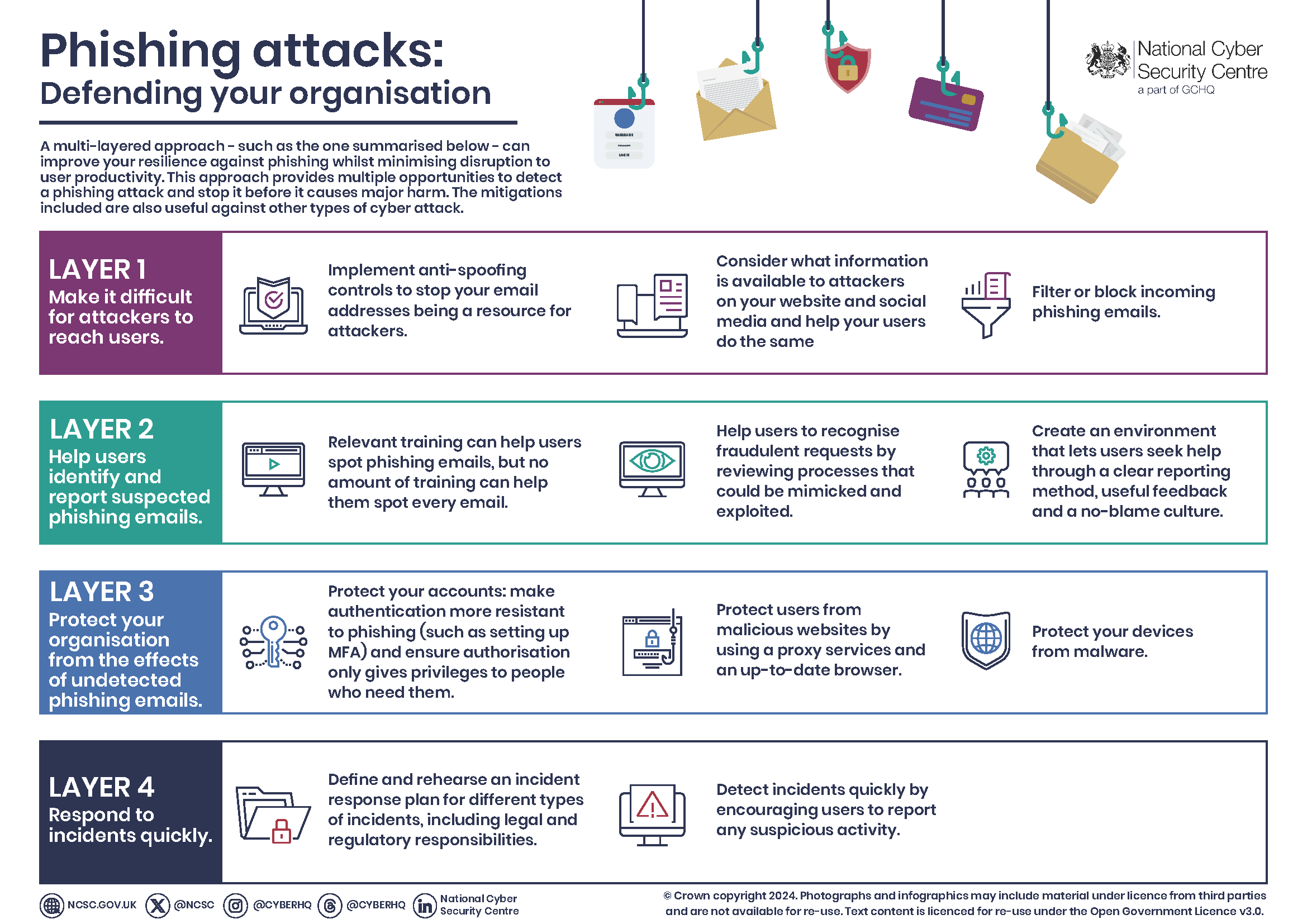
The mitigations below require a combination of technological, process, and people-based approaches. They all must be considered for your defenses to be really effective. More specifically, the NCSC guidance splits the mitigations into four layers on which you can build your defenses:
- Make it difficult for attackers to reach your users
- Help users identify and report suspected phishing messages
- Protect your organization from the effects of undetected phishing emails
- Respond quickly to incidents
- If you can’t implement all of the mitigations, try to address at least some of the mitigations from within each of the layers.
The Problems with Phishing Simulations
According to the UK’s Nation Cyber Security Centre: No training package, including phishing simulations, can teach users to spot every phishing attempt. Asking users to examine, in-depth, every email they receive will not leave enough hours in the day for work tasks. It’s an unrealistic and counter-productive goal because responding to emails and clicking links is an integral part of work.
Phishing simulations can also create legal risks. Since no one can be expected to spot all phishing emails, punishing people for clicking on emails you’ve sent starts to resemble entrapment. For this reason, you should always check with your HR department before undertaking any phishing simulations (the NPSA has a set of free resources to help you design training.)
More practically, blaming users for clicking on links doesn’t work. People click for a range of reasons. These could be personality traits or situational (for example, if a person is busy and stressed). Threatening someone with punishment doesn’t change these factors.
Phishing simulations also erode trust between employees and security. Employees who are afraid for their jobs will not report mistakes. Employees should instead create a positive cyber security culture so employees feel comfortable reporting phishing incidents, and in this sense, they can be a valuable early warning system.
So why are phishing simulations so popular? One reason is that they allegedly provide clear, quantitative metrics that demonstrate how progress (in an area you care about) is being made. However, metrics express an organization’s values or biases, and if you appear to value the absence of reports of problems, you incentivize people to keep quiet about issues. You should consider how you can formulate your security metrics to also include successes. For example, as well as measuring how many people clicked on a phishing email, focus on how many people reported it.
Four Layers of Mitigation
Layer 1: Make it difficult for attackers to reach your users
This section describes the defenses that can make it difficult for attackers to even reach your end users.
Don’t let your email addresses be a resource for attackers
Attackers ‘spoof’ trusted emails, making their emails look like they were sent by reputable organizations (such as yours). These spoofed emails can be used to attack your customers or people within your organization.
How do I do this?
Make it harder for email from your domains to be spoofed by employing the anti-spoofing controls: DMARC, SPF and DKIM, and encourage your contacts to do the same.
Reduce the information available to attackers
Attackers use information freely available on your website and social media accounts (known as your ‘digital footprint’) to make spear-phishing messages more convincing.
How do I do this?
Consider what visitors to your website need to know, and what detail is unnecessary (but could be useful for attackers). This is particularly important for high-profile members of your organization, as this information could be used to craft personalized whaling attacks (a type of spear phishing that targets a ‘big phish’, such as a board member who has access to valuable assets).
Help your staff understand how sharing their personal information can affect them and your organization, and develop this into a clear ‘digital footprint policy’ for all users. The NPSA’s Digital Footprint Campaign contains a range of useful materials that can help with this.
Be aware of what your partners, contractors, and suppliers give away about your organization online.
Filter or block incoming phishing emails
Emails should be filtered/blocked for spam, phishing, and malware before they reach your users. Ideally, this should be done on the server, but it can also be done on devices (ie in the mail client). Filtering services usually send emails to spam/junk folders, while blocking services ensure that they never reach your user. The rules determining blocking or filtering will need to be fine-tuned for your organization’s needs.
How do I do this?
For inbound email, anti-spoofing policies of the sender’s domain should be honored. If the sender has a DMARC policy in place with a policy of quarantine or reject, then you should do as requested if validation checks fail.
If you use a cloud-based email provider, ensure that their filtering/blocking service is sufficient for your needs and that it is switched on by default for all your users. If you host your own email server, ensure that a proven filtering/blocking service is in place. This can be implemented locally and/or purchased as a cloud-based service. Again, ensure that it is switched on by default for all your users.
If you filter all suspicious emails to spam/junk folders, users will have to manage a large number of emails, adding to their workload and leaving open the possibility of clicking on a bad link. However, if you block all suspicious emails, some legitimate emails could get lost. You may have to change the rules over time to ensure the best compromise, and to respond to your business’s changing needs and ways of working.
Filtering email on devices can offer an additional layer of defense against malicious emails. However, this should not compensate for ineffective server-based measures, that could block a large number of incoming phishing emails entirely.
Email can be filtered or blocked using a variety of techniques including IP addresses, domain names, email address allow/deny list, public spam and open relay deny lists, attachment types, and malware detection.
Layer 2: Help users identify and report suspected phishing emails
This section outlines how to help your staff spot phishing emails, and how to improve your reporting culture.
Carefully consider your approach to phishing training
Training your users – particularly in the form of phishing simulations – is the layer that is often over-emphasized in phishing defenses. However, spotting all phishing emails is hard, and spear phishing attacks are even harder to detect. The advice given in many training packages (based on standard warnings and signs) will help your users spot some phishing emails, but they can’t teach everyone to spot all phishing emails.
How do I do this?
Ensure that your users understand the nature of the threat posed by phishing, especially those departments that may be more vulnerable to it.
Customer-facing departments may receive high volumes of unsolicited emails, whereas staff authorized to access sensitive information, manage financial assets, or administer IT systems will be of greater interest to an attacker (and maybe the target of a sophisticated spear phishing campaign). Ensure these more vulnerable staff are aware of the risks, and offer them additional support.
Help your users identify the common features of phishing messages. The NCSC has produced guidance on how to spot scam messages.
Don’t reprimand users who are struggling to recognize phishing emails. Users who fear reprisals will not report mistakes promptly, if at all.
Training should reassure users that they won’t get in trouble if they report phishing incidents. This message needs buy-in across all departments including HR, support, and senior management.
Rather than using simulations, some companies ask participants to craft their own phishing emails, giving them a much richer view of the influence techniques used. A friendly competition between peers can avoid unhelpful ‘us vs them’ scenarios that phishing simulations may engender, where staff may feel they are being tested by the security team.
Make it easier for your users to recognize fraudulent requests
Attackers can exploit ‘ways of working’ to trick users into handing over information (including passwords), or making unauthorized payments. Consider which processes could be mimicked by attackers, and how to review and improve them so phishing attacks are easier to spot.
How do I do this?
Ensure staff are familiar with the normal ways of working for key tasks (such as how payments are made), so they’re better equipped to recognise unusual requests.
Make processes more resistant to phishing by ensuring that all important email requests are verified using a second type of communication (such as SMS message, a phone call, logging into an account, or confirmation by post or in-person). Other examples of changing processes include using a different login method, or sharing files though an access-controlled cloud account, rather than sending files as attachments.
Think about how your outgoing communications appear to suppliers and customers. Can your recipients easily distinguish your genuine email from a phishing attack? Is the recipient expecting an email, and will they recognise your email address? Do they have any way of knowing if links are genuine?
Consider telling your suppliers or customers what to look out for (such as ‘we will never ask for your password’, or ‘our bank details will not change at any point’). This gives the recipient another chance to detect a phish.
Create an environment that encourages users to report phishing attempts
Building a culture where users can report phishing emails (including where they’ve been clicked on) gives you vital information about what types of phishing attacks are being used. You can also learn what types of emails are getting mistaken for phishing, and what impact this might be having on your organization.
How do I do this?
Have an effective process for users to report phishing. Is the process clear, simple, and quick to use? Quickly provide feedback on what action has been taken, and make it clear that their contributions make a difference.
Think about how you can use informal communication channels (through colleagues, teams, or internal message boards) to create an environment where it is easy for users to ‘ask out loud’ for support and guidance when they may be faced with a phishing attempt.
Avoid creating a punishment or blame-oriented culture around phishing. It is important that users feel supported to come forward even when they have ‘clicked’ and later believe that something may be suspicious.
Layer 3: Protect your organization from the effects of ‘successful’ phishing emails
Since it’s not possible to stop all attacks, this section outlines how to minimize the impact of phishing emails that reach your users and are clicked.
Protect your devices from malware
Malware is often hidden in phishing emails, or in websites that they link to. Well-configured devices and good end-point defenses can stop malware from installing, even if the email is clicked. Some defenses are specific to particular threats (such as disabling macros) and some may not be appropriate for all devices (anti-malware software may be pre-installed on some devices and not needed on others). Finally, the impact of malware on your wider system will depend on how your system has been set up. For more information, refer to the section on reducing the impact of compromise from our Secure design principles.
How do I do this?
Prevent attackers from using known vulnerabilities by only using supported software and devices. Make sure that software and devices are always kept up to date with the latest patches.
Prevent users from accidentally installing malware from a phishing email, by limiting administrator accounts to those who need those privileges. People with administrator accounts should not use these accounts to check email or browse the web.
Protect your users from malicious websites
Links to malicious websites are often a key part of a phishing email. However, if the link is unable to open the website, then the attack cannot continue.
How do I do this?
Most modern browsers will block known phishing and malware sites. Note that is not always the case on mobile devices.
Organizations should run a proxy service, either in-house or in the cloud, to block any attempt to reach websites that have been identified as hosting malware or phishing campaigns.
Public sector organizations should use the Public Sector DNS service, which will prevent users from resolving domains known to be malicious.
Protect your accounts with effective authentication and authorization
Passwords are a key target for attackers, particularly if they are for accounts with privileges such as access to sensitive information, handling financial assets, or administering IT systems. You should make your login process to all accounts more resistant to phishing, and limit the number of accounts with privileged access to the absolute minimum.
How do I do this?
Add additional security to your login process by setting up multi-factor authentication (MFA), which is also called ‘two-step verification (2SV)’ on some web services. Having a second factor means that an attacker cannot access an account using just a stolen password.
Consider using password managers, some of which can recognize real websites and will not autofill on fake websites. Similarly, you could use a single sign-on method (where the device recognizes and signs into the real website automatically). Adopting these techniques means that manually entering passwords becomes unusual, and a user can more easily recognize a suspicious request.
Consider using alternative authentication mechanisms (like biometrics or smartcards) that require more effort to steal than passwords. The damage an attacker can cause is proportionate to the privileges allocated to the credentials they have stolen. Only provide privileged access to people who need it for their roles. Regularly review these and revoke privileges if no longer needed. Remove or suspend accounts that are no longer being used, such as when a member of your organization leaves or moves to a new role.
Consider reviewing your password policies. Doing so may (for example) reduce the chance likelihood of staff re-using passwords across home and work accounts.
Layer 4: Respond quickly to incidents
All organizations will experience security incidents at some point, so make sure you’re in a position to detect them quickly, and to respond to them in a planned way.
Detect incidents quickly
Knowing about an incident sooner rather than later allows you to limit the harm it can cause.
How do I do this?
Ensure users know in advance how they can report incidents. Bear in mind that they may be unable to access normal means of communication if their device is compromised.
Use a security logging system to pick up on incidents your users are not aware of. To collect this information, you can use monitoring tools built into your off-the-shelf services (such as cloud email security panels), build an in-house team, or outsource to a managed security monitoring service.
Smaller organizations that may lack dedicated logging resources may wish to try CISA’s Logging Made Easy open source project, which provides a practical way to set up basic end-to-end Windows monitoring of your IT estate.
Once a monitoring capability has been set up, it needs to be kept up to date to ensure it remains effective.
Have an incident response plan
Once an incident is discovered, you need to know what to do to prevent any further harm as soon as possible.
How do I do this?
Ensure that your organization knows what to do in the case of different types of incidents. For example, how will you force a password reset if the password is compromised? Who is responsible for removing malware from a device, and how will they do it? For more information, refer to the NCSC’s Incident Management guidance.
Incident response plans should be practiced before an incident occurs. The best way to do this is through exercising. If you’re new to this, the NCSC has created Exercise In A Box, a free online tool that helps you to find out how resilient you are to cyber attacks, and lets you practice in a safe environment.
Case study: example of multi-layered phishing mitigations
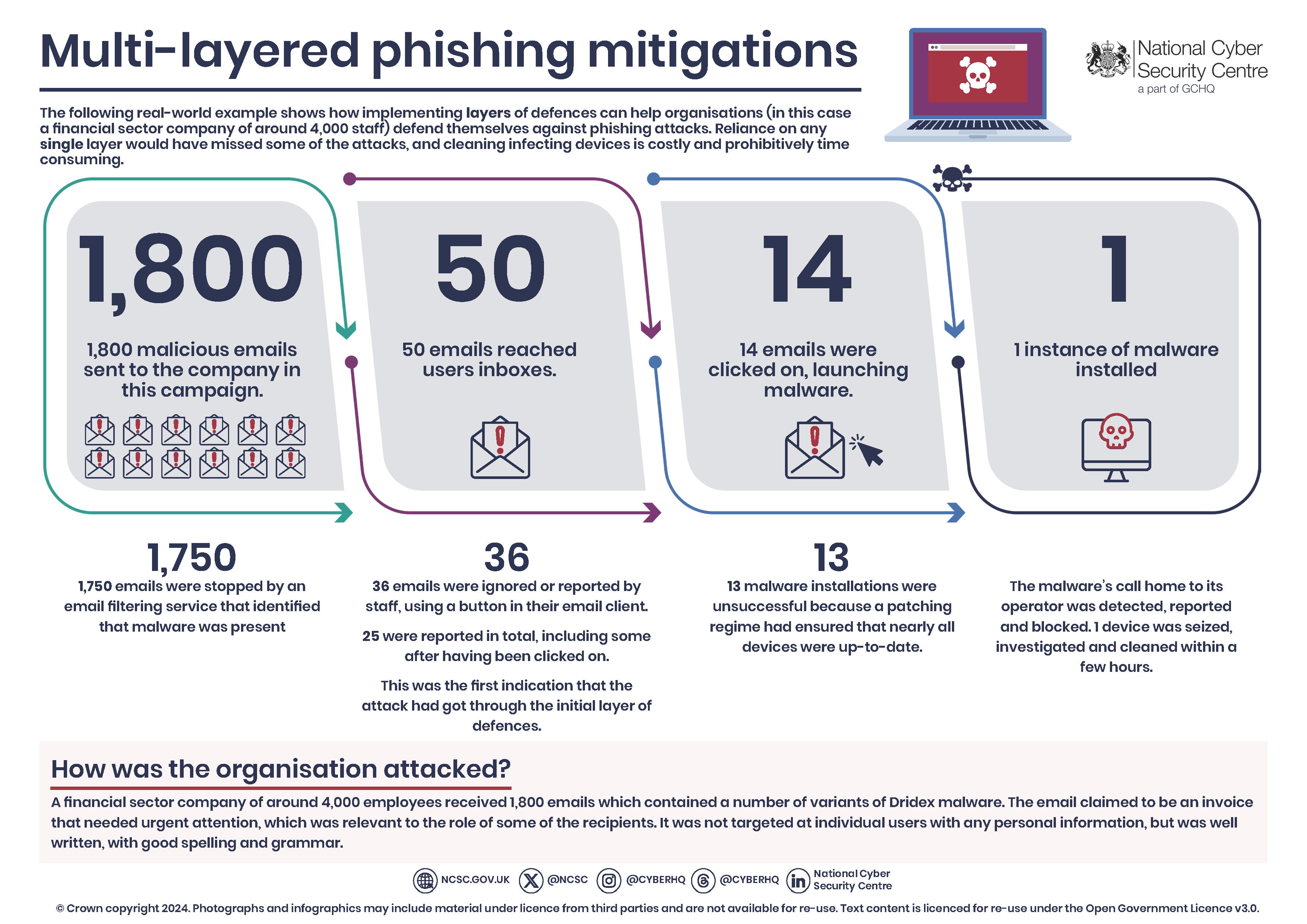
The following real-world example illustrates how a company in the financial sector used effective layered mitigations to defend against phishing attacks. Reliance on any single layer would have missed some of the attacks and resulted in a costly and time-consuming clean-up operation.
The company, which has around 4,000 employees, received 1,800 emails containing a number of variants of Dridex malware. The email claimed to be an invoice that needed urgent attention, which was relevant to the role of some of the recipients. It was not targeted at individual users with any personal information, but was well written, with good spelling and grammar.
Summary of the phishing attack:
- 1,800 emails were sent to the organization by this campaign
- 1,750 were stopped by an email filtering service that identified that malware was present.
- This left 50 emails that reached user inboxes.
- Of these, 36 were either ignored by users or reported using a button in their email client. 25 were reported in total, including some post-click; this was the first indication that the attack had got through the initial layer of defenses.
- This left 14 emails that were clicked on, which launched the malware.
- 13 instances of the malware failed to launch as intended due to devices being up-to-date.
- 1 instance of malware was installed.
- The malware’s call home to its operator was detected, reported, and blocked.
- 1 device was seized, investigated, and cleaned in a few hours.
-/ 30 /-
What do you think about this?
Please share your thoughts in a comment below!
Table of Contents
- Guarding the Gate: Strategies to Defend Your Organization from Phishing Attacks and Email Scams
- Article Abstract
- Guarding the Gate: Strategies to Defend Your Organization from Phishing Attacks and Email Scams
- Introduction – What is a Phishing Attack?
- Why You Need a Multi-layered Approach
- The Problems with Phishing Simulations
- Four Layers of Mitigation
- Layer 1: Make it difficult for attackers to reach your users
- Layer 2: Help users identify and report suspected phishing emails
- Layer 3: Protect your organization from the effects of ‘successful’ phishing emails
- Layer 4: Respond quickly to incidents
- Case study: example of multi-layered phishing mitigations
LEAVE A COMMENT?
Recent Comments
On Other Articles
- Arwyn Lautenschlager on Love Bombing And How Romance Scam Victims Are Forced To Feel: “I was love bombed to the point that I would do just about anything for the scammer(s). I was told…” Feb 11, 14:24
- on Dani Daniels (Kira Lee Orsag): Another Scammer’s Favorite: “You provide a valuable service! I wish more people knew about it!” Feb 10, 15:05
- on Danielle Delaunay/Danielle Genevieve – Stolen Identity/Stolen Photos – Impersonation Victim UPDATED 2024: “We highly recommend that you simply turn away form the scam and scammers, and focus on the development of a…” Feb 4, 19:47
- on The Art Of Deception: The Fundamental Principals Of Successful Deceptions – 2024: “I experienced many of the deceptive tactics that romance scammers use. I was told various stories of hardship and why…” Feb 4, 15:27
- on Danielle Delaunay/Danielle Genevieve – Stolen Identity/Stolen Photos – Impersonation Victim UPDATED 2024: “Yes, I’m in that exact situation also. “Danielle” has seriously scammed me for 3 years now. “She” (he) doesn’t know…” Feb 4, 14:58
- on An Essay on Justice and Money Recovery – 2026: “you are so right I accidentally clicked on online justice I signed an agreement for 12k upfront but cd only…” Feb 3, 08:16
- on The SCARS Institute Top 50 Celebrity Impersonation Scams – 2025: “Quora has had visits from scammers pretending to be Keanu Reeves and Paul McCartney in 2025 and 2026.” Jan 27, 17:45
- on Scam Victims Should Limit Their Exposure To Scam News & Scammer Photos: “I used to look at scammers photos all the time; however, I don’t feel the need to do it anymore.…” Jan 26, 23:19
- on After A Scam, No One Can Tell You How You Will React: “This article was very informative, my scams happened 5 years ago; however, l do remember several of those emotions and/or…” Jan 23, 17:17
- on Situational Awareness and How Trauma Makes Scam Victims Less Safe – 2024: “I need to be more observant and I am practicing situational awareness. I’m saving this article to remind me of…” Jan 21, 22:55
ARTICLE META
Important Information for New Scam Victims
- Please visit www.ScamVictimsSupport.org – a SCARS Website for New Scam Victims & Sextortion Victims
- Enroll in FREE SCARS Scam Survivor’s School now at www.SCARSeducation.org
- Please visit www.ScamPsychology.org – to more fully understand the psychological concepts involved in scams and scam victim recovery
If you are looking for local trauma counselors please visit counseling.AgainstScams.org or join SCARS for our counseling/therapy benefit: membership.AgainstScams.org
If you need to speak with someone now, you can dial 988 or find phone numbers for crisis hotlines all around the world here: www.opencounseling.com/suicide-hotlines
A Note About Labeling!
We often use the term ‘scam victim’ in our articles, but this is a convenience to help those searching for information in search engines like Google. It is just a convenience and has no deeper meaning. If you have come through such an experience, YOU are a Survivor! It was not your fault. You are not alone! Axios!
A Question of Trust
At the SCARS Institute, we invite you to do your own research on the topics we speak about and publish, Our team investigates the subject being discussed, especially when it comes to understanding the scam victims-survivors experience. You can do Google searches but in many cases, you will have to wade through scientific papers and studies. However, remember that biases and perspectives matter and influence the outcome. Regardless, we encourage you to explore these topics as thoroughly as you can for your own awareness.
Statement About Victim Blaming
SCARS Institute articles examine different aspects of the scam victim experience, as well as those who may have been secondary victims. This work focuses on understanding victimization through the science of victimology, including common psychological and behavioral responses. The purpose is to help victims and survivors understand why these crimes occurred, reduce shame and self-blame, strengthen recovery programs and victim opportunities, and lower the risk of future victimization.
At times, these discussions may sound uncomfortable, overwhelming, or may be mistaken for blame. They are not. Scam victims are never blamed. Our goal is to explain the mechanisms of deception and the human responses that scammers exploit, and the processes that occur after the scam ends, so victims can better understand what happened to them and why it felt convincing at the time, and what the path looks like going forward.
Articles that address the psychology, neurology, physiology, and other characteristics of scams and the victim experience recognize that all people share cognitive and emotional traits that can be manipulated under the right conditions. These characteristics are not flaws. They are normal human functions that criminals deliberately exploit. Victims typically have little awareness of these mechanisms while a scam is unfolding and a very limited ability to control them. Awareness often comes only after the harm has occurred.
By explaining these processes, these articles help victims make sense of their experiences, understand common post-scam reactions, and identify ways to protect themselves moving forward. This knowledge supports recovery by replacing confusion and self-blame with clarity, context, and self-compassion.
Additional educational material on these topics is available at ScamPsychology.org – ScamsNOW.com and other SCARS Institute websites.
Psychology Disclaimer:
All articles about psychology and the human brain on this website are for information & education only
The information provided in this article is intended for educational and self-help purposes only and should not be construed as a substitute for professional therapy or counseling.
While any self-help techniques outlined herein may be beneficial for scam victims seeking to recover from their experience and move towards recovery, it is important to consult with a qualified mental health professional before initiating any course of action. Each individual’s experience and needs are unique, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another.
Additionally, any approach may not be appropriate for individuals with certain pre-existing mental health conditions or trauma histories. It is advisable to seek guidance from a licensed therapist or counselor who can provide personalized support, guidance, and treatment tailored to your specific needs.
If you are experiencing significant distress or emotional difficulties related to a scam or other traumatic event, please consult your doctor or mental health provider for appropriate care and support.
Also read our SCARS Institute Statement about Professional Care for Scam Victims – click here to go to our ScamsNOW.com website.















Thank you for your comment. You may receive an email to follow up. We never share your data with marketers.